Objectives
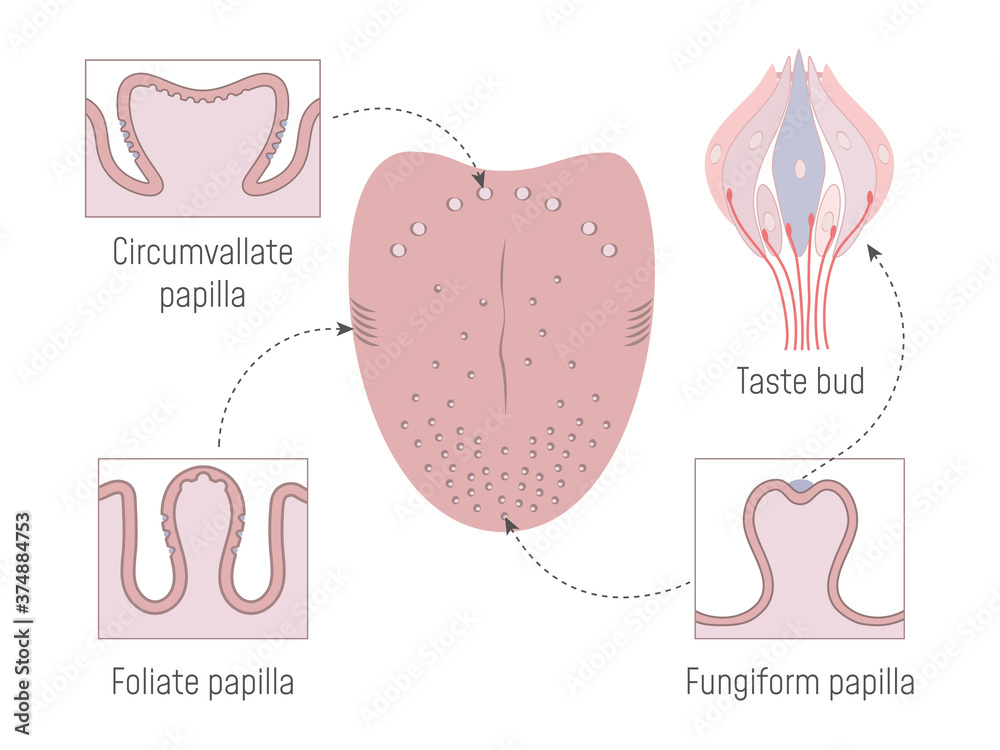
2947 Describe the distribution of taste buds in the tongue.
- circumvalate
- folate
- fungiform
- filiform
2948 Recognize the features suggestive of a benign or malignant neoplasm of the salivary glands.
- benign
- painless mass
- slow growing
- malignant
- painful mass
- can also be slow growing
- facial nerve palsy
- lympadenopathy
- skin involvement
2949 Describe the nerve supply to the tongue including motor, sensory and special sensory components.
- motor
- sensory
- solitary nucleus (receives all peripheral taste nerves)
- cranial nerves
- anterior 2/3 of tongue: facial nerve (VII)/ chorda tympani
- posterior 2/3: glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
- small area on epiglottis: vagus nerve (X)
- peripheral nerves
- anterior 2/3: lingual nerve (V3) to trigeminal nucleus
- posterior 2/3: pharyngeal brancges of glossopharyngeal nerve
2950 Describe the location of the major and minor salivary glands and indicate the nerve supply to the major salivary glands.
- major salivary glands
- parotid
- stenson’s duct at 2nd molar
- parasympathetic innervation: glossopharyngeal nerve, auriculotemporal nerve, parotid gland
- submandibular
- wharton’s duct under tongue
- superior salivatory nucleus, facial nerve, submandibular ganglion
- sublingual
- duct of rivinus
- superior salivatory nucleus, facial nerve, submandibular ganglion
- minor salivary glands

2952 List the functions of saliva and list 3 causes of xerostomia.
- functions of saliva
- lubricate
- helps mastication and swallowing
- helps articulate
- taste
- oral hygiene
- protective role (IgA)
- xerostomia causes
- medications
- head and neck cancer
- Sjogren’s syndrome
2955 Define sialadenitis and sialolithiasis and know the presenting features of each.
- sialadenitis
- infection of salivary gland (most common parotid)
- presentation:
- sudden onset of gland enlargement
- induration
- tenderness
- +/- purulent saliva at duct opening
- sialolithiasis
- stones in salivary gland/duct
- presentation:
- painful swelling with eating, resolves
- can be infected


